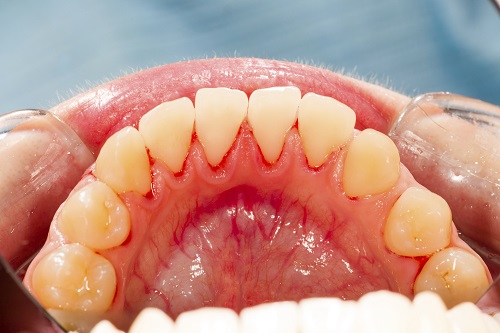
Together with tooth decay, gum disease is an enemy of oral health. When not caught early and treated, gum infection can progress and ultimately cause tooth loss. Although gum disease is prevalent among all people, one group is particularly at an increased risk of suffering from the disease. This group includes smokers and tobacco users.
How Smoking Contributes To Gum Disease
Smokers unlike non-smokers are less likely to show inflammation and redness, which are the initial signs of a progressing gum infection. Constriction of blood vessels prevents the delivery of sufficient oxygen as well as nutrients to the gum tissues. The gums may appear pink and healthy, while an infection is still present. When this is the case, you may have a delay in diagnosis of your gum disease, allowing the periodontal disease to advance.
Last but not least, smoking tends to interfere with gum disease treatment. Due to nicotine, an infection or a wound in the mouth of a tobacco user will heal slower than normal. Combined with delayed diagnosis of gum disease, the slow healing time makes smokers lose their teeth from gum infection.
How To Prevent Gum Disease
You can avoid gum disease by observing good dental habits such as brushing teeth not less than twice a day. Make sure you floss to help remove plaque. It is crucial that you see our dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups. And if you smoke, it is the right time to quit.
Letting a dentist know about your smoking habit can help with your dental care or treatment. Quitting smoking can help improve your oral health while lowering the risk of gum disease.
When visiting us for dental checkups, exams, and treatment, make sure you let our periodontist know about your smoking habit and how long you have been doing it. Contact us today for your dental treatment.